Token Takeaway: DFI;
DeFiChain is a decentralised version of a commercial bank with its blockchain platform anchored to Bitcoin. In addition to being decentralised, it is also accessible to anyone, anywhere around the world. This second and final article of the DeFiChain series will examine the governance of DeFiChain, recent developments, its weaknesses, a take on its future outlook and more.
In part I, I gave an overview of the current financial system (CeFi and DeFi), introduced the background and foundation of DeFiChain, and examined the tokenomics of the DFI token. Part I sets the context for this article, so if you haven’t read it already, I highly recommend that you do.
Governance
In a truly decentralised fashion, DeFiChain’s governance system allows community stakeholders to vote on DeFi Improvement Proposals (DFIPs). Using a fair and democratic governance system means that DeFiChain can evolve in the best interests of its users and stakeholders. 20,000 DFI is needed to vote, while 10 DFI is required to submit a Community Fund proposal.
There are around 10,909 enabled masternodes, and each masternode gets one vote on improvement proposals as they previously would have deposited 20,000 DFI at stake. Voting is carried out by signing a message with a digital signature unique to each masternode. Currently, the process is done on GitHub, an open-source repository for programming files. DeFiChain previously announced that voting was to be moved on-chain by the end of Q1 2022, but there haven’t been any updates as of yet.
The DeFiChain Foundation, the team behind the protocol, is responsible for issuing tokens and is governed by an independent board selected through masternodes votes. The DeFiChain Foundation will also be tasked with assessing applications from ecosystem partners and providing foundation grants in the form of DFI coins to developers and contributors of DeFiChain. The community development fund, created by the DeFiChain Foundation, will be used for the development, marketing, and research of the project, as determined by its community members.
In June 2021, with the intention to establish on-chain governance and further decentralise DeFiChain, DFIP #7 stated that the “DeFiChain Foundation should no longer be the custodian of [the foundation treasury] coins and should therefore be destroyed”. Following the results of DFIP #7, 273.7 million DFI has been burned and will be redistributed into circulation via block rewards over time, without affecting the total supply of DFI (1.2 billion).
Recent Developments
In 2021, DeFiChain experienced the highest development activity amongst major DeFi projects. Their achievements so far include:
- listing on major exchanges
- approving multiple DeFi improvement proposals (DFIPs)
- adding multiple pool pairs for liquidity mining
- becoming 100% carbon neutral
- launching the new dTokens.
- Burning and redistribution of 273.7 million DFI, which were previously held in the Foundation Wallet.
- De-registration of DeFiChain Foundation from Singapore.
Additionally, data from Staking Rewards shows over 30% of the total DFI in circulation, i.e. $663.5m, is being staked, making DeFiChain the 31st largest coin by total staked value. Higher staking adds more security and efficiency to the blockchain, making it more resistant to attacks and strengthening its ability to process transactions.
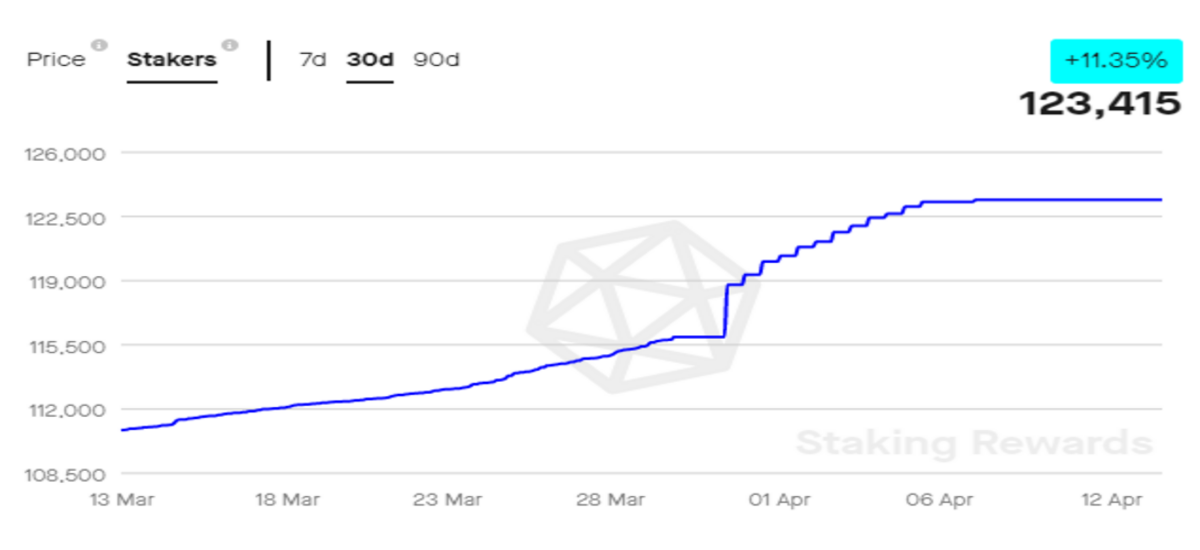
As we can see in the above graph, the unique number of addresses delegating DFI saw significant growth in the past 30 days. A steady increase in stakers indicates the growing adoption of DFI.
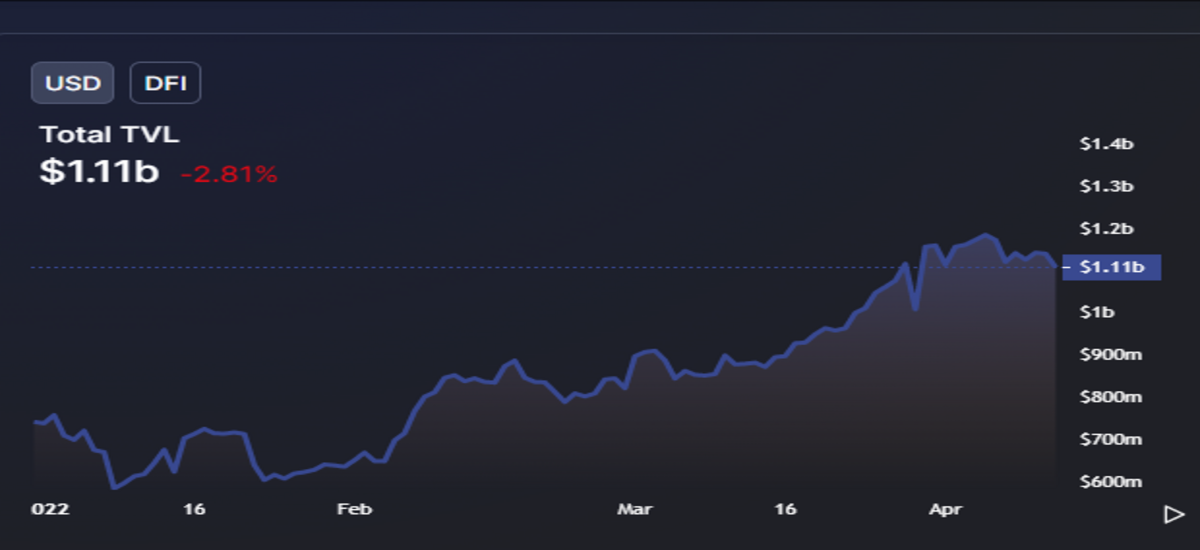
According to data from DeFiLama, DeFiChain has $1.1bn in TVL, seeing continuous gradual growth. Recently, one of the biggest sources of momentum for DFI has been the launch of decentralised assets on the DeFiChain network and staking options for holders. Platform users now have access to multiple pools that not only include large-cap cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum but synthetic versions of popular stocks and indices, including pairs for Tesla, Apple, the S&P500 and more.
Nasdaq, alongside Finnhub and Tiingo, will be providing price feeds for these stock tokens.
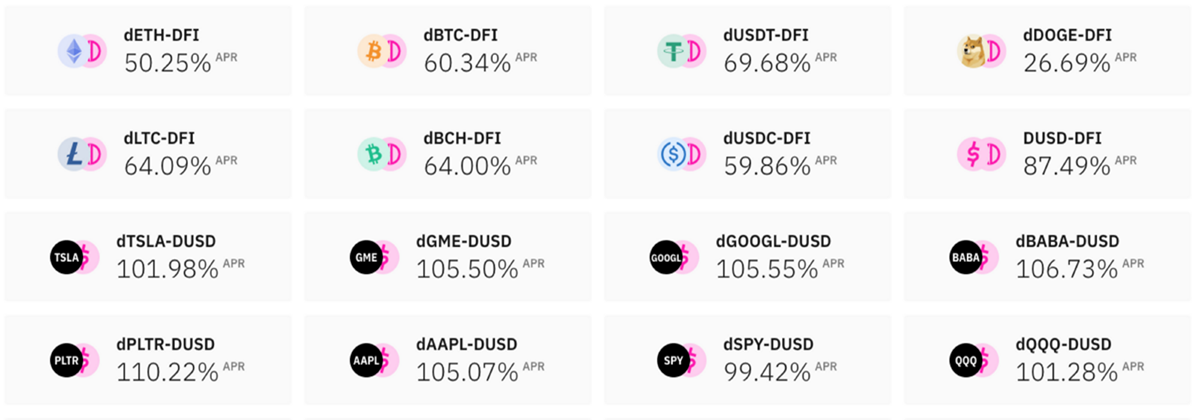
In addition to having exposure to these assets, users also benefit from staking them with significantly higher-than-average yields available on the platform. Due to high demand, dTokens were trading at a 10%-15% premium over the price of corresponding assets. However, the launch of the Fort Canning Road hard fork fixes this issue by implementing new code upgrades. Other d-asset options that are available to users include gold, silver, the ARK Innovation ETF, and the iShares 20+ Year Treasury Bond ETF.
With all-new updates and developments in the project, the daily transaction throughput has also seen a surge from last year.
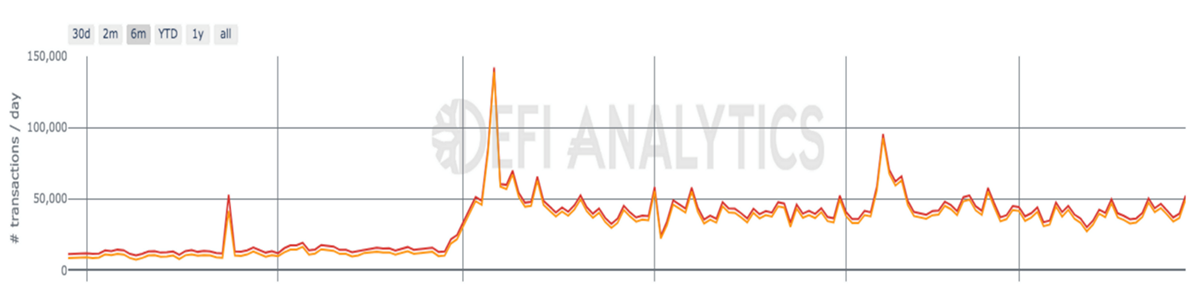
As seen in the above chart, daily transactions were around 11k in September 2021, while March 2022 saw an average of 41k, which is significant growth in only 6 months. For the all-time high in December 2021, daily transactions reached over 142k. Meanwhile, the recent surge in February 2022 recorded a high of around 95k transactions per day following the launch of decentralised tokens.
Cake DeFi, a private company in Singapore, was an early ecosystem partner for DeFiChain. In early March 2022, they launched a new corporate venture arm, Cake DeFi Ventures (CDV), with $100 million in capital. CDV will focus its investments across Web3, metaverse, NFTs, gaming, esports and fintech. Its user base grew to over 400,000 in 2021, and $230 million in rewards was paid out to customers in the same year. By the end of 2022, the company plans to increase customer pay-outs by 74% or more, which equals to around $400 million.
Concerns
However, affiliation to bitcoin may also have some shortcomings, like speed, scalability, and supporting complex smart contracts. DeFiChain claims to tackle these issues by keeping its own consensus mechanism and function set. Currently, it can process over 2,200 TPS, compared to Bitcoin’s 5. Meanwhile, its Fintech competitor VISA can process around 65k TPS, which marks a drastic limitation in DeFiChain’s scalability. In terms of competition, we can identify Terra ecosystem, Fantom, AAVE, PancakeSwap, MakerDAO as the most serious contenders. Technically DeFiChain also competes with TradFi and Fintech organisations.
The competition in this space will only grow in the future, many new projects will be launched, but not all will survive. That being said, the DeFi sector is too big to be harnessed by any 1 of the contenders. There is a high chance that there will be multiple successful players in the space. However, only time will tell which of these projects will be on that list.
DFI staking feature is one of the biggest attractions of DeFiChain due to its high APY of 32.6%. This APY is generated via the issuance of new tokens. However, the APY will be generated by transaction costs when all the coins are issued. Depending on the number of on-chain transactions, the yield could significantly decrease when this happens. Perhaps unsurprisingly, the APY is not sustaining its high yield and has recently been declining from its highs.
DeFiChain benefits for users and developers
The current state of DeFi is populated by general-purpose blockchains, most of which provide Turing-complete command sets for the development of smart contracts on the chain. General-purpose blockchains require a large amount of coding to provide financial services, increasing the risk of hackability or bugs in the code. Functionalities that are basic requirements for financial services, such as multisig, are often difficult to implement or missing on general-purpose blockchains. Usage of Turing-complete command sets requires developers to create complex programs to develop any application. For example, to create a P2P lending contract on top of MakerDAO, a programmer requires approximately 2,000 lines of code. Any bug in that code can have drastic consequences, such as loss of funds.
Maintaining such a large codebase means that there is a more significant chance for mistakes and a large attack surface for even simple apps. Therefore, while being a dedicated PoS consensus blockchain, DeFiChain also leverages the best aspects of PoW, that is, using hashing of the staking node’s ID for block creation. This is achieved by DeFiChain being a dedicated non-Turing-complete blockchain designed specifically for the decentralised finance (DeFi) industry by being a single purpose blockchain. The DeFiChain Foundation also gives out grants for developers in the form of DFI.
Derivatives outlook
By the end of Q2, DeFiChain plans to offer derivatives on the platform. The derivatives industry has recently been making headlines. In January 2022, the derivatives market volumes remained steady at $2.86tn, whilst spot volumes declined significantly (down 30.2% to $1.81tn). As a result, derivative markets reached an all-time high market share of 61.2%, breaking the previous all-time high of 57.3% in November 2020.
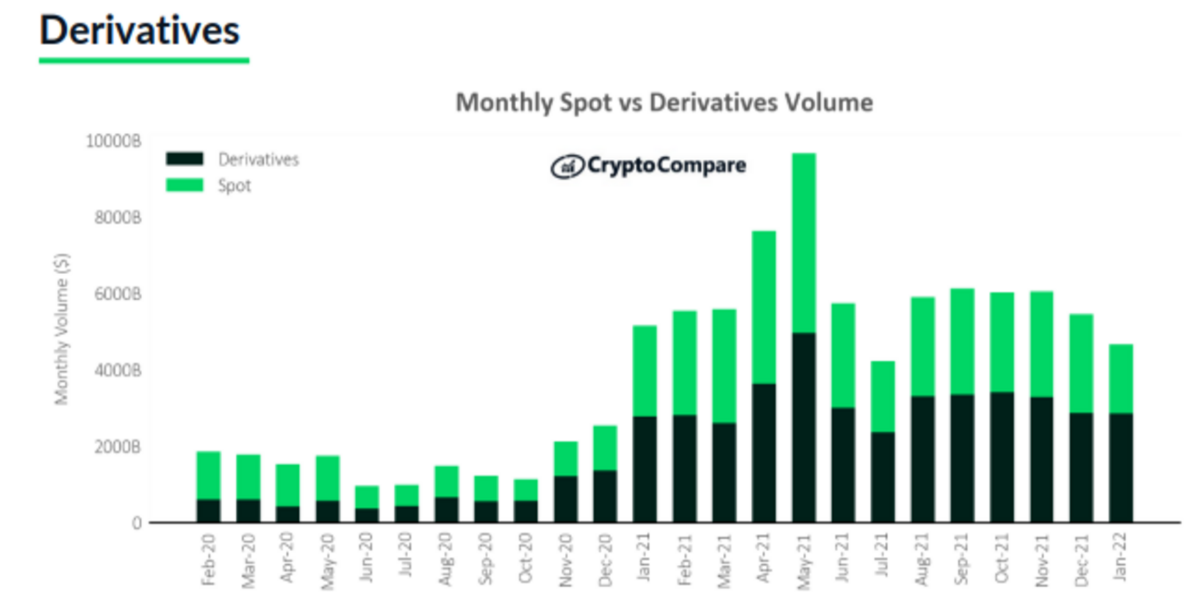
Source: CryptoCompare. Monthly Spot and Derivatives volumes.
In the third quarter of 2020, the trading volume of the cryptocurrency derivatives market reported an increase of 25.1% from the previous quarter, and a year-on-year increase of 159.4% from the third quarter of 2019.
Due to high volatility in the crypto market, the ability to both hedge positions and enter speculative trades is attractive to traders. Derivatives serve this purpose, hence their growth and the huge potential opportunity for DeFiChain if it manages to take market share.
Key points of DeFiChain
- a massive scalable and energy conserving consensus.
- fast transactions and high security.
- ability to create a variety of DeFi apps based on one chain, rapidly and with a very low attack surface.
- multi-token support on one chain through decentralised wrapped token technology.
- decentralized governance.
- independence of other financial systems and financial instruments.
- fully liquid investments with no minimum size of investments and no minimum lock-up periods.
- Rapid development of dApps with dedicated calls specifically for finance applications.
- Highly immutable – by periodic anchoring to Bitcoin blockchain.
- blockchain is not used for any type of non-financial dApps, thus decisions of Foundation and developers are focused 100% on decentralised financial use cases and nothing else.
- DeFiChain Foundation gives grants to developers who are developing functionality for DeFiChain or dApps to run on the blockchain.
Future
Last year, the DeFi market grew by 47% and shows no signs of stopping. Compared to its competitors, DeFiChain is still in the early stages, leaving plenty of room for growth. As outlined in their roadmap, the protocol has some interesting plans lined up for this year. These plans included on-chain governance, a desktop light wallet, offering derivatives, supporting the Ethereum Virtual Machine, NFTs, and ledger for light wallet. Furthermore, their long-term plans include decentralised leverage (10x - 50x), implementing financial derivatives as native on-chain transactions, creating secondary markets and blockchain for P2P transactions, an on-chain automated clearing house (ACH), and real-time gross settlement (RTGS) and blockchain transactions across all financial institutions, sovereign states and countries.
Conclusion
The DeFi sector grows more interesting with every new development. After all, DeFi was born from the mistakes of TradFi and Fintech. DeFiChain is positioning itself as a bridge between financial services and users, removing intermediaries. If DeFiChain continues to take market share and grow at a similar pace, I believe it will quickly catch up with its competitors. Their services will not only benefit users in first-world countries but especially in developing countries where financial services are unfamiliar privileges to most.