Polygon: More Than Just a Scaling Solution

Disclaimer: Your capital is at risk. This is not investment advice.
Token Takeaway: MATIC Token;
As the leading smart contract blockchain, Ethereum struggles with scalability and high costs, which will only become more pronounced with growing crypto adoption. This is a problem that Layer-2 scaling solutions like Polygon were created to fix. Polygon offers a range of EVM-compatible scaling solutions and boasts some of the best scalability features in the industry. This Token Takeaway takes a closer look at the fundamentals of Polygon and its native token MATIC.
Overview
The Matic Network was launched in 2017 by Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun and Mihailo Bjelic with the primary vision to improve and enhance the Ethereum infrastructure. In 2021, the company was rebranded to Polygon to reflect its expanded scope. Today, Polygon is the leading Layer-2 (L2) scaling solution platform for Ethereum, providing a developer-friendly environment that allows developers to create and scale decentralised applications and other blockchain projects that are secure, highly scalable, and user-friendly.
Polygon has rapidly risen in ranking and is now among the top 10 largest projects by market capitalisation, surpassing established networks such as TRON, Solana, and Polkadot. However, the recent success of the Ethereum Merge and its advancements towards scalability has caused some to question the long-term sustainability of Polygon. Given Ethereum's ambitious goals for scalability, will ETH 2.0 make Polygon redundant in the future?
The WHY and HOW?
Ethereum faces challenges due to high activity on the network, particularly during the launch of highly anticipated NFT projects or dApps. This leads to increased gas fees and poor network performance, making it difficult for users to engage with smart contracts on the blockchain and for dApps to scale and offer affordable services. To address these limitations, ETH 2.0 was introduced as a major upgrade to improve Ethereum’s speed and reduce costs.
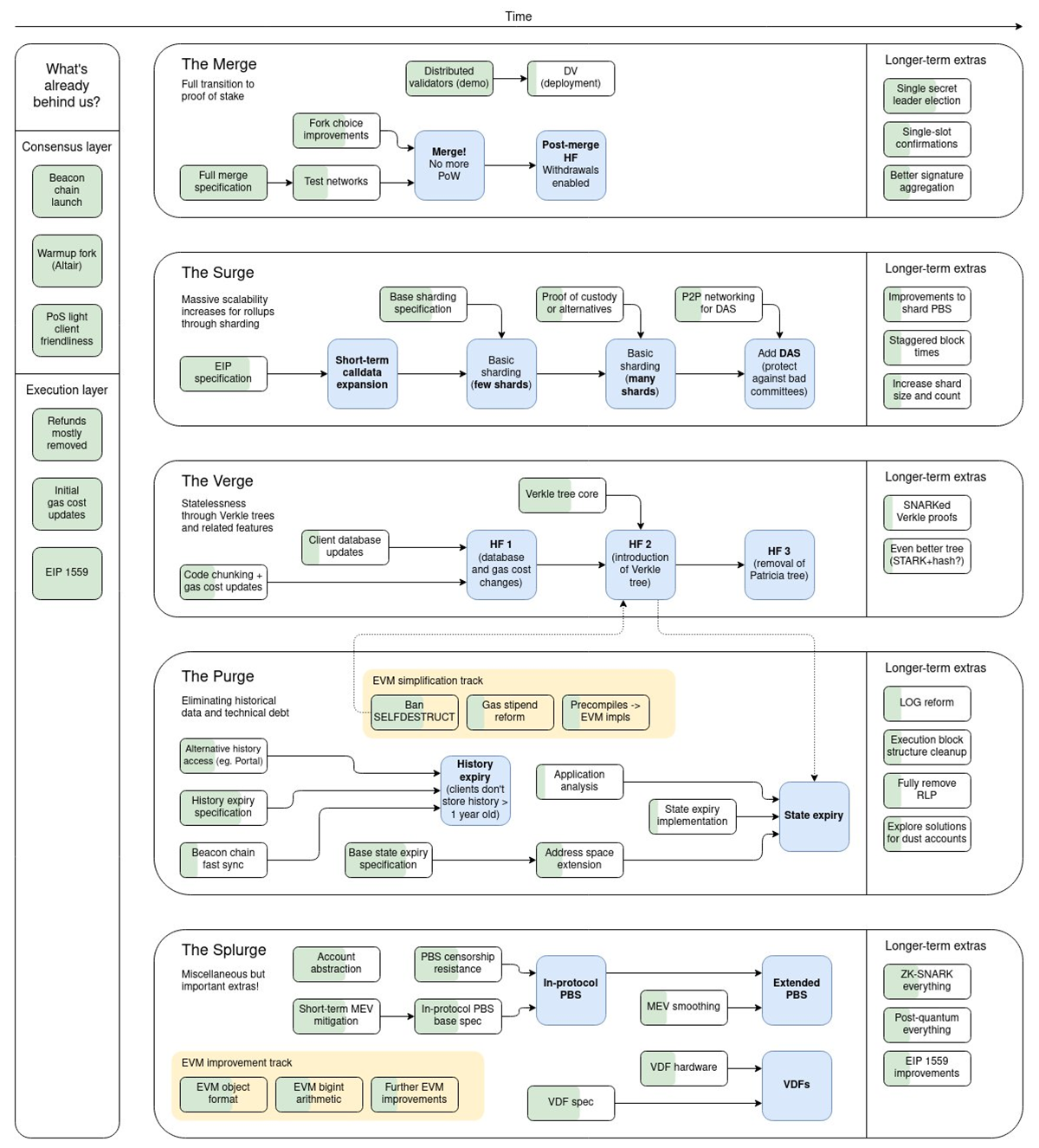
The first phase, “The Merge”, successfully transitioned Ethereum from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) on 15 September 2022, with additional upgrades set to be implemented in the future. However, even if all ETH 2.0 phases are 100% successful, the goal of 1 billion crypto users by 2030 could easily breach Ethereum’s capacity. In that scenario, sharding and L2 scaling solutions could assist Ethereum by offering off-chain computation to increase its throughput and efficiency.
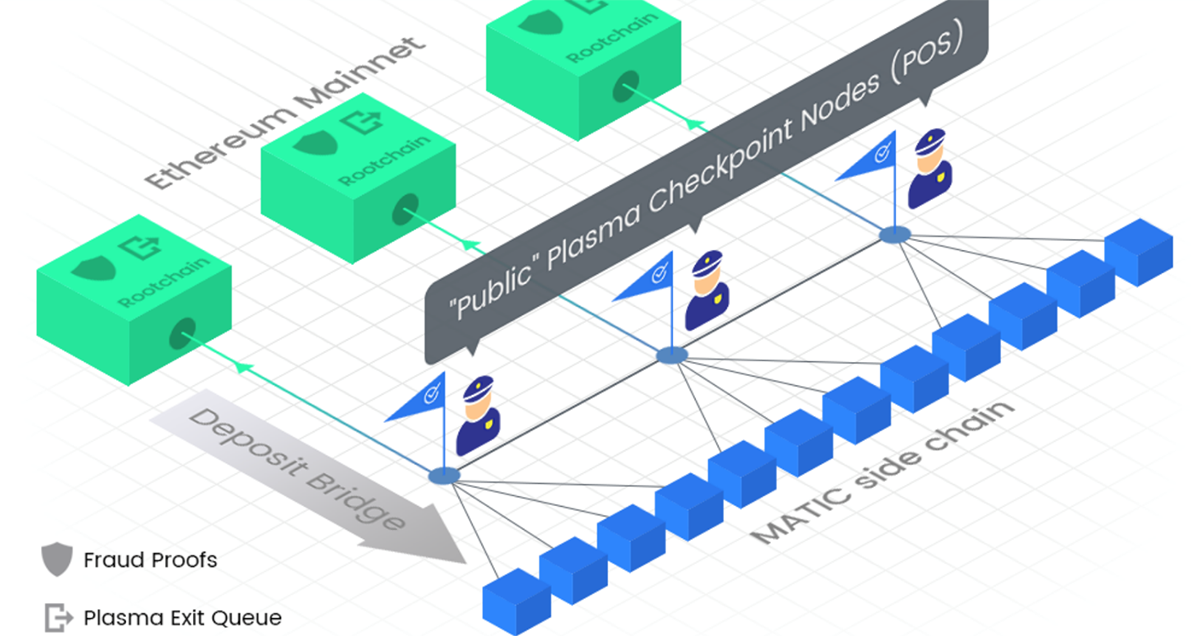
Polygon, also known as Ethereum’s Internet of Blockchains, inherently exists to improve the efficiency and performance of Ethereum dApps and make the best aspects of Ethereum accessible to everyone. The flagship product, Polygon PoS, uses a 3-layer architecture to provide hybrid PoS and Plasma-enabled sidechains (a separate blockchain that runs alongside the primary blockchain, in this case, Ethereum). As seen in the infographic below, Polygon PoS leverages security from Ethereum and offers up to 7,000 TPS using sidechains, compared to Ethereum’s 15 TPS. Moreover, Polygon PoS uses a decentralised set of validators, capped at 100, to verify transactions and create blocks, solving Ethereum’s infamous blockchain trilemma.
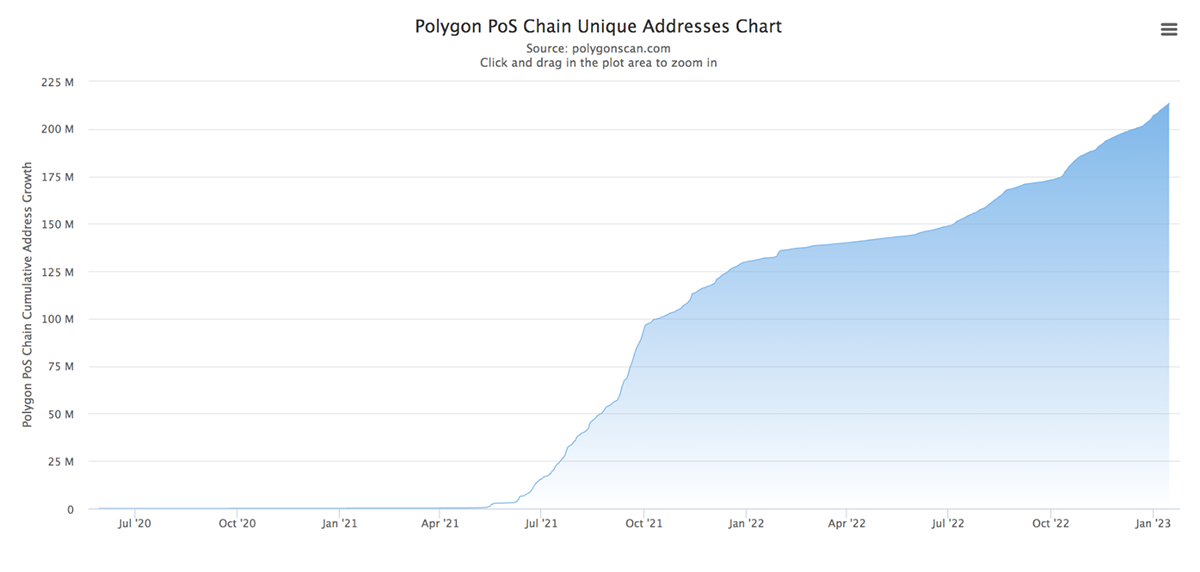
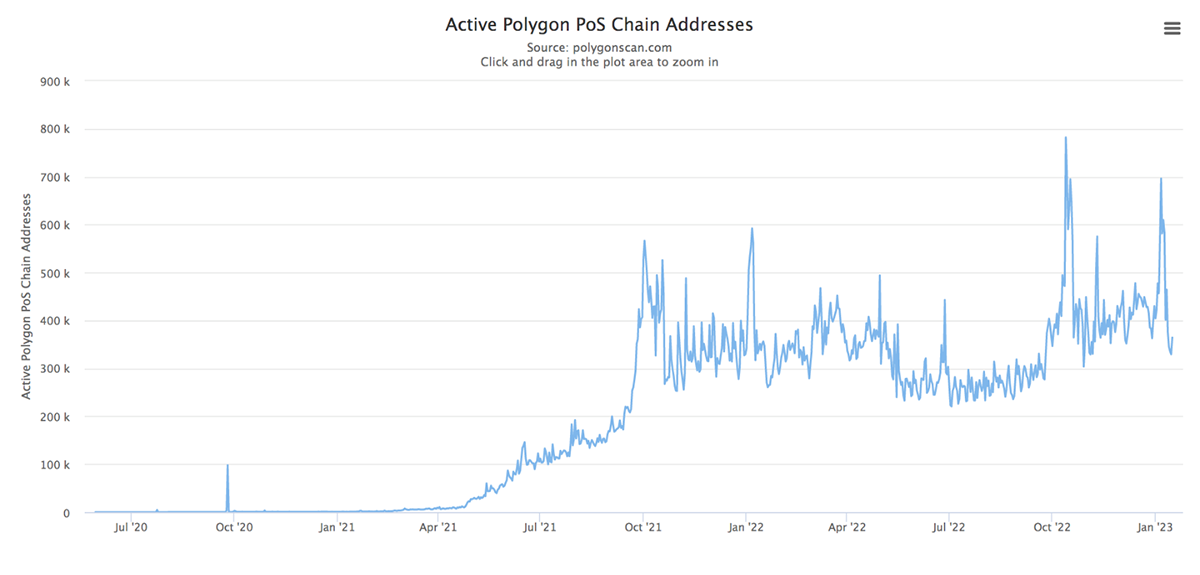
Polygon PoS now has over 213 million unique addresses, of which over 360k are active daily. The network has processed over 1.4 billion transactions since its launch in 2019, with transaction fees around 10,000x lower than Ethereum. Utilising the Polygon PoS is an optimal method for scaling Ethereum dApps as it offers high levels of security, scalability, adaptability, affordability, and full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Moreover, Polygon launched the Polygon SDK in May 2021 with a vision to make Ethereum a fully-fledged multi-chain system. This is similar to Polkadot and Cosmos but with additional benefits such as high security, Ethereum ecosystem access, and more robust architecture. Polygon SDK will also serve as a framework for launching new chains based on any Ethereum scaling solution, including Optimistic Rollups, zk-Rollups, and Validium. Polygon SDK will also support and connect standalone chains (Ethereum sovereign chains).
In addition to Polygon PoS, the platform also offers seven different scaling solutions:
| Name | Description |
| Polygon zkEVM | A type of zk-Rollup that allows for the same user experience as the Ethereum Network but with added security. The source code is open source. |
| Polygon Avail | Standalone chains can use Avail to ensure the security of their validators by making all necessary data readily accessible. |
| Polygon Edge | An adaptable and customisable system for the creation of both private and public blockchain networks that are compatible with the Ethereum Network. |
| Polygon Nightfall | A Privacy-Focused hybrid Optimistic-ZK rollup for Enterprises. |
| Polygon Miden | A rollup technology that utilises STARKs for zero-knowledge proof and supports arbitrary smart contracts. |
| Polygon Zero | A ZK L2 scaling solution that uses Plonky2 to provide faster and more decentralised performance. It offers two modes, rollup and validium, to increase transaction speed and reduce costs for users. |
| Polygon Supernets | It simplifies the process of creating a blockchain by offering expert assistance and eliminating the need for maintaining blockchain infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on building blockchains without hassle. |
Source: Polygon. Polygon L2 scaling solutions.
Tokenomics
MATIC, Polygon’s native token, was publicly launched in an Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) on Binance in April 2019, raising $5m. Around the same period, another 380 million MATIC were allocated in a seed funding round and early supporters round, raising an additional $610k. More recently, in February 2022, Polygon raised a whopping $450m in a funding round led by Sequoia Capital India. The funds were raised through a private sale of MATIC, which was supported by the industry’s top names, including SoftBank’s Vision Fund, Galaxy Digital, Republic Capital, Dragonfly Capital, Unacademy, Alan Howard, Dune Ventures, and many others.
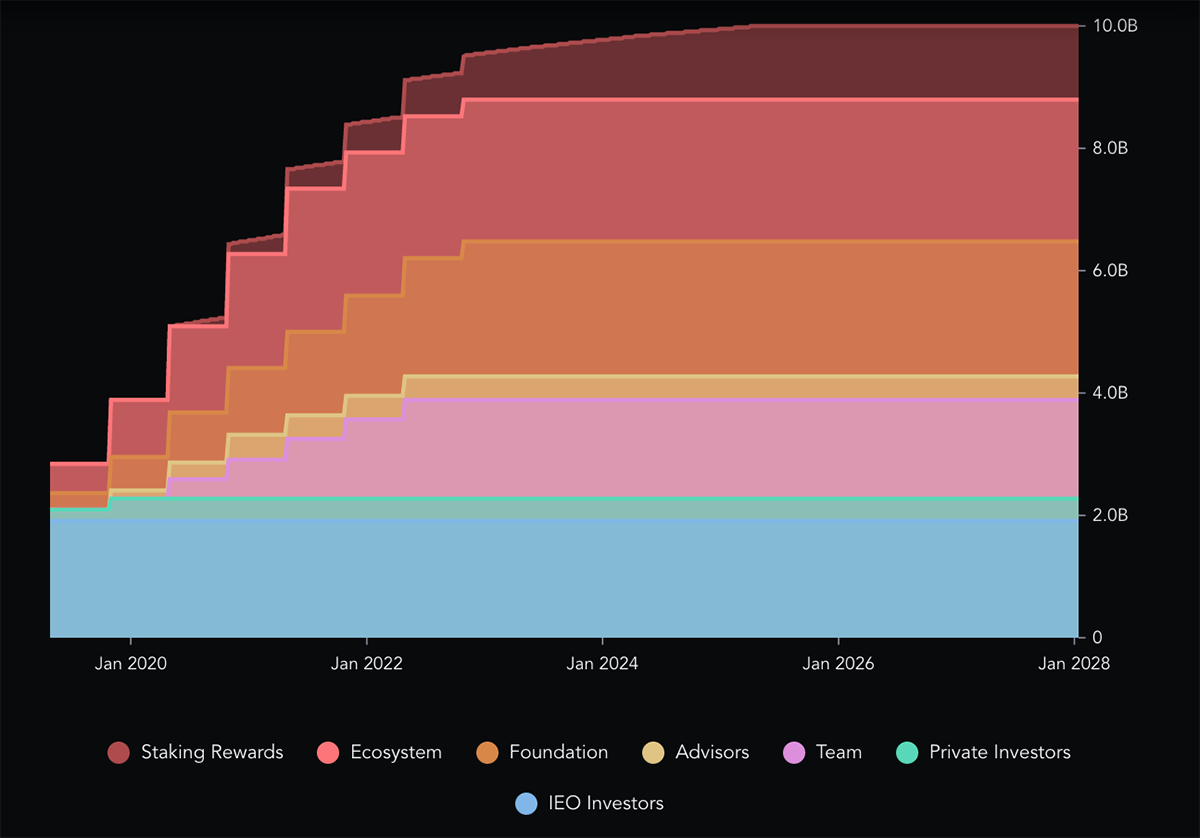
The total max supply of MATIC is 10 billion, with 8.9 billion currently available in the market. The remaining 1.1 billion will be issued periodically in the coming years. Over 3.5 billion MATIC tokens worth around $3.5bn are staked on Polygon for an APY of 4.95%, removing a huge chunk of supply from circulation. This makes it the 6th largest crypto token in terms of staking market cap. As of today, the 100 Validators and 23k+ Delegators have earned just under $700m in rewards from staking. Moreover, with the EIP-1559 upgrade, the base transaction fees, which vary depending on network congestion, is permanently sent to a burn contract. As of today, over 5.7 million MATIC tokens have been burned.
Apart from securing Polygon chains via staking, MATIC is also used for paying gas fees on Polygon chains and gives governance rights to token holders.
On 17 January 2023, Polygon PoS underwent a hard fork to combat high gas fees during periods of high activity and to reduce the time required for each transaction to be finalised. Although a decrease in gas fees results in lower burning of MATIC, it will ultimately benefit the network as the consistent gas fees will encourage more people to use it.
Ecosystem
The Polygon ecosystem has 1703 dApps in sectors including NFTs, GameFi, DeFi, B2B, Developer tools, and more. According to their website, over 37k dApps have used Polygon to scale and enhance performance.

Currently, Polygon is one of the leading platforms for NFTs in the industry. Many renowned institutions and individuals have launched their NFT projects on the platform. The number of users on Polygon’s OpenSea marketplace for NFTs has surpassed 1.5 million. Additionally, since December 2022, over 2 million NFTs have been sold on Polygon, generating more than $22.4 million in sales. Moreover, in January 2022, Polygon sold over 2.6 million NFTs, surpassing Ethereum by over 400k NFTs.
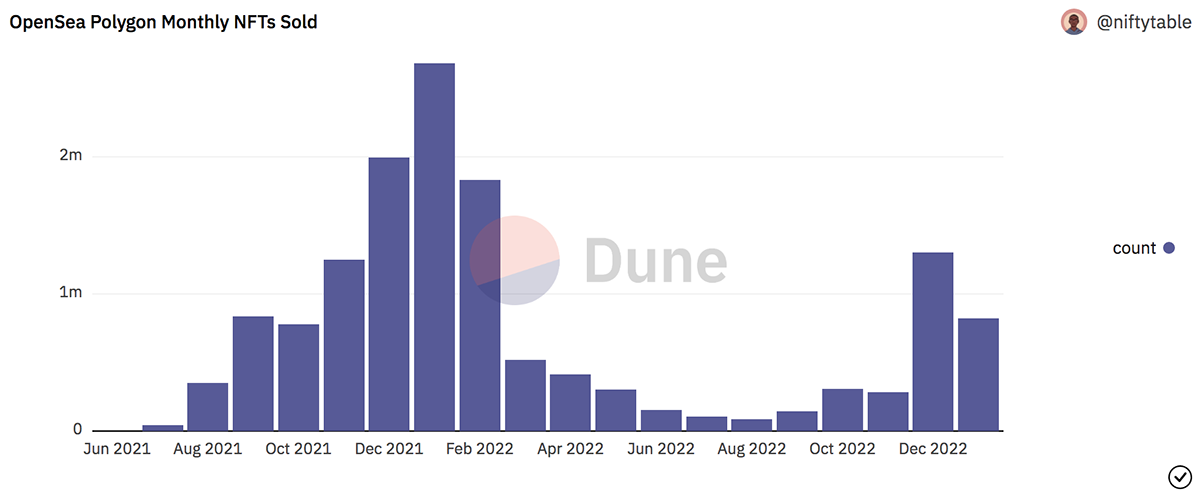
As illustrated in the above chart, activity is slowly starting to pick up again in Q4 2022. There is a particularly notable increase in December 2022, which I will discuss further in the “Partnerships” section below.
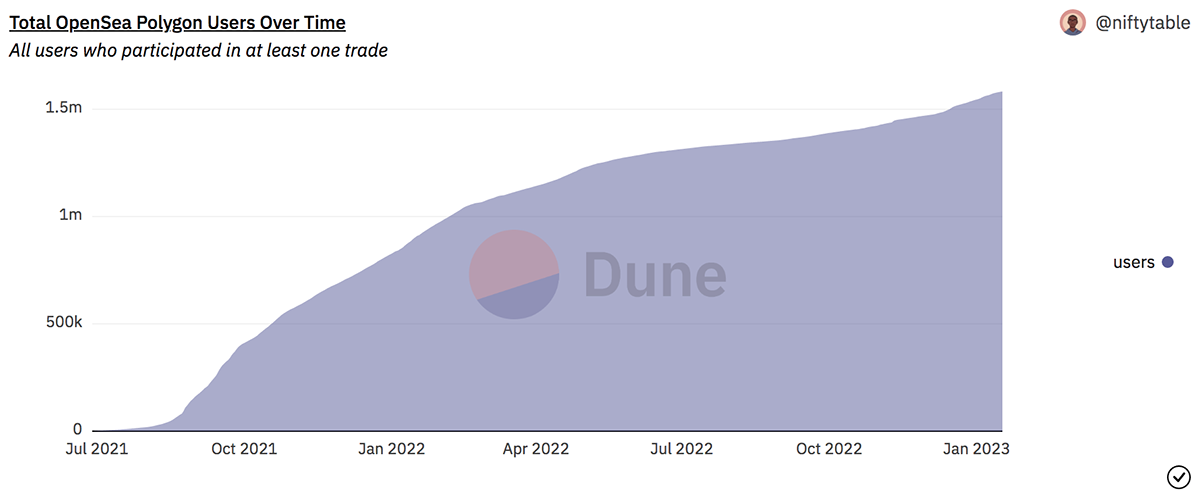
The number of Polygon NFT users has also seen steady growth since July 2021, as highlighted in the above chart.
Moreover, decentralised exchanges (DEXs) on Polygon processed over $1.3bn in volume in December 2022. The largest DEX on Polygon by volume is Uniswap, with a 75.1% market share, followed by QuickSwap (8.6%) and Kyber (7.3%).
Lastly, the total value locked (TVL) on Polygon is currently $1.6bn, which is small compared to its all-time high of $14.1bn in June 2021. Among the assets locked on the platform, AAVE has the largest share, representing 25.8% of the total TVL, with a value of $414m.
Partnerships
Based on the number of major institutions building on Polygon, the platform’s robust technical and fundamental environment attracts investors and developers.

DeLabs, the creators of the successful Solana-based NFT projects DeGods and Y00ts, has been given a $3m grant by Polygon to move Y00ts to the network. The transition, which is scheduled to take place in Q1 2023, is expected to attract Solana NFT users to Polygon.
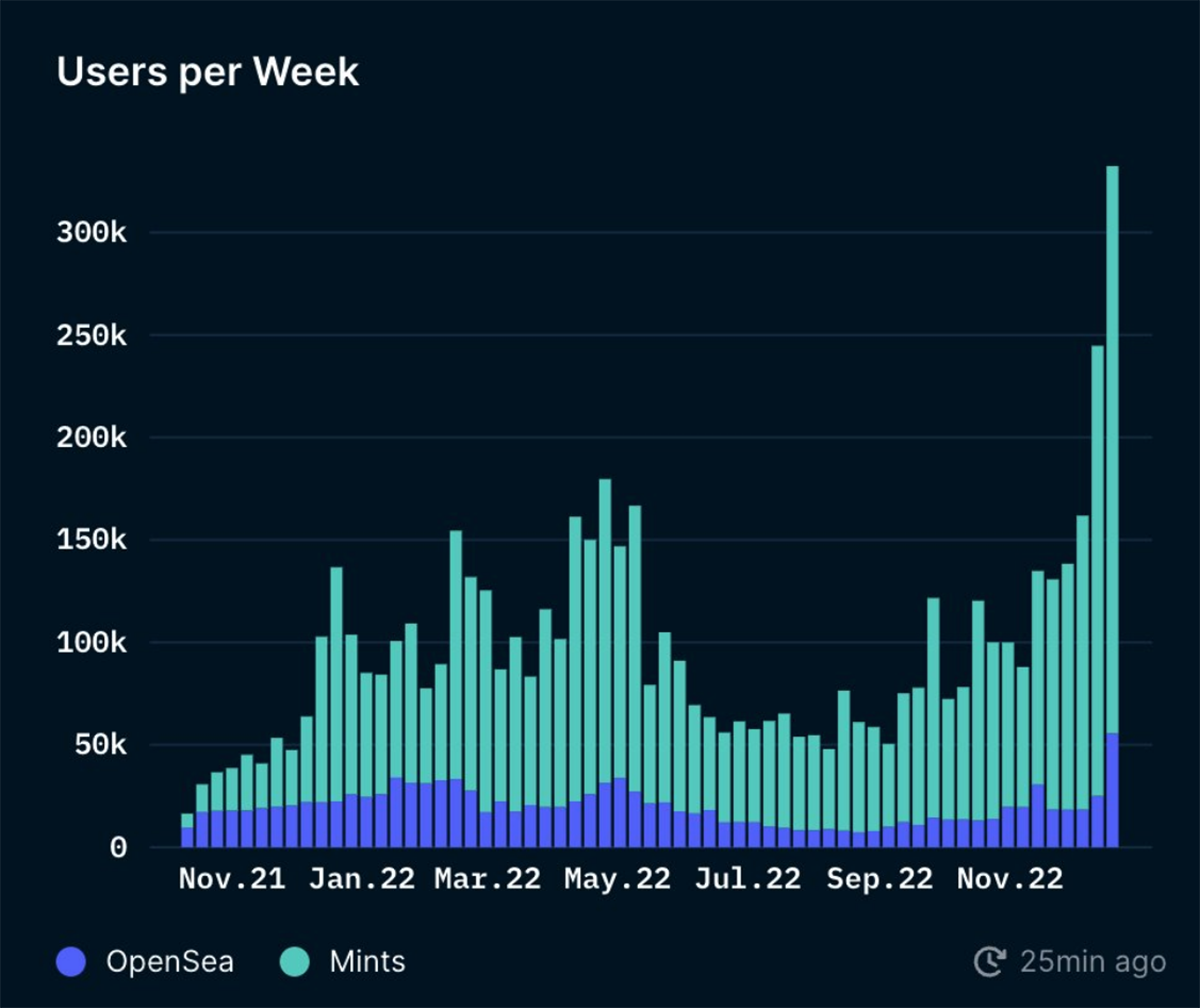
Additionally, on 15 December 2022, Donald Trump minted a collection of 45,000 NFTs on Polygon called “Trump Digital Trading Cards”. The individual NFTs were priced at $99, and the collection sold out the following day. This release resulted in a significant increase in the number of Polygon NFT users, with over 332,000 users participating in NFT trading or minting on Polygon within the same week.
Conclusion
It’s clear that Polygon is already positively regarded among top VCs, institutions, and individuals, highlighting the prominence and reputation that Polygon has in the industry. With its suite of scaling solutions and favoured technical features, it has already managed to onboard thousands of dApps and NFT projects onto the platform. As more individuals and entities begin to utilise and develop on Polygon chains, there will be a corresponding increase in the usage of MATIC. With such an increase in network activity, MATIC holds significant potential for growth.
Provided all ETH 2.0 phases are successfully implemented, Polygon could see a reduction in growth to some extent. Still, there is almost zero to no chance that it would render the network obsolete. That being said, it’s essential that Polygon continues to onboard dApps and other blockchain-based projects to strengthen its platform and keep up with the times. As we all know, the crypto industry moves at lightning speed.

Comments ()