Render Network: Revolutionising the World of GPU Rendering

Disclaimer: Your capital is at risk. This is not investment advice.
Token Takeaway: RNDR Token
The Render Network is the leading crypto-native distributed rendering platform that operates on an incentive-based economic model, enabling individuals to perform GPU-based rendering jobs on the network. Creators (clients) can assign their rendering tasks to node operators on the Render Network for a fee. This Token Takeaway will examine the fundamentals of the Render Network and its native token, RNDR.
Overview
Rapid technological advancements and improved computational capabilities have allowed us to create marvellous graphics with virtual and augmented realities that are almost indistinguishable from reality. Driven by the burst in popularity of smartphones and other high-resolution devices, we can now experience Ultra High-Definition (UHD) graphics in movies, images, and games at our fingertips. But the rendering (i.e. the process of generating a final image or video output from a 3D model) of these graphics is no easy feat. In fact, the amount of work required to generate UHD 8K at 240 frames per second is 256 times more than that needed for HD 720p at 30 frames. Moreover, for larger and more complex jobs requiring high frame rates and resolutions, such as animations and virtual reality walkthroughs, external servers and additional resources are often necessary.
Enter Render Network, an efficient, cost-effective and decentralised 3D-rendering solution. With origins dating back to 2009, the Render Network was officially publicly launched in April 2020. With a mission to democratise the future of digital content creation, the Render Network works to improve global usage of Graphics Processing Units, or GPUs (a specialised type of computer processor designed to handle complex calculations required for rendering graphics and images). Render is used by some famous digital content creators like Beeple and Pak. Moreover, according to a Global Market Insights report, GPU as a service market is currently valued at around $5bn and is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30% for the next 10 years, reaching over $80bn in valuation.
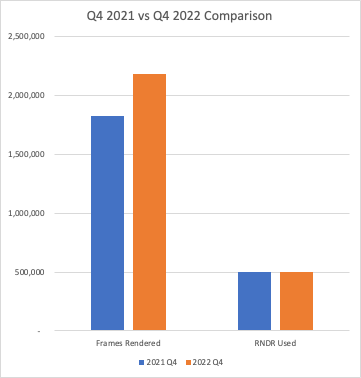
According to a recent report published by Render, the overall network usage grew by 10% from Q3 to Q4 2022, with an increase of 5% in user retention. The total frames rendered have also seen significant yearly growth in 2022 (9.4 million) compared to 2021 (5.9 million). Additionally, the network has experienced many scalability improvements, resulting in a 50% reduction in failure rates and a 50-75% increase in performance.
What Problem Does Render Network Solves?
Render Network’s core purpose is to solve the problem of inefficient usage of GPUs for rendering graphics and images. Traditionally, rendering has been a complex and computationally intensive process, requiring significant hardware resources, which has made it difficult and costly for smaller creators. Additionally, larger creators may have idle hardware resources that are not being used, leading to inefficient resource usage from both a monetary aspect and an environmental one.
The Render Network provides a decentralised cloud rendering marketplace that connects creators in need of rendering resources with those who have idle GPUs. By leveraging blockchain technology and using an incentive-based economic model, the Render Network allows individuals to perform GPU-based rendering jobs on the network, which is monetised through fees. This creates a more efficient usage of GPU resources and reduces costs for creators, making rendering more accessible to a wider range of individuals and businesses.
Another problem that the Render Network addresses is the lack of transparency and security in traditional rendering methods. The use of blockchain technology provides a secure, transparent and encrypted platform for digital content creators to access rendering services. This eliminates the risk of fraud and ensures that costs associated with the job are fair.
How Does Render Network Work?
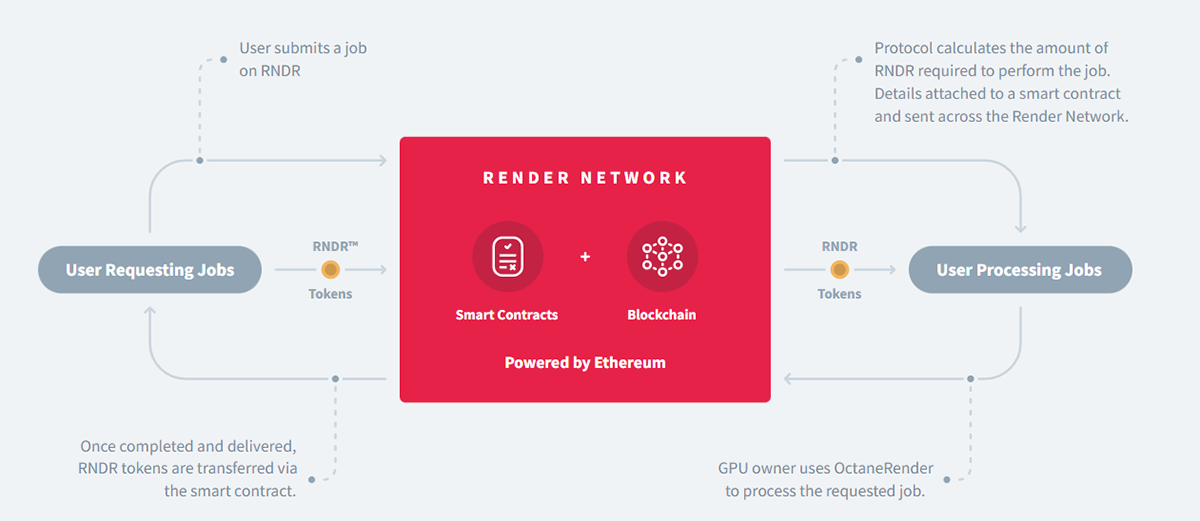
Uploading the Job
Creators (clients) upload their 3D-rendering tasks, which contain specific parameters, in ORBX file format through OctaneRender (a GPU rendering engine created by OTOY, the company behind Render Network) onto the platform. Creators can also choose which service tier they want based on their job’s priority level and Node Operators’ reputation score (performance and reliability on the network). Finally, after the job is uploaded, all its details and terms are broadcasted to the network through a smart contract with all the necessary specifications.
Assigning and Completing the Job
Render’s Multi-Tier Pricing (MTP) protocol automatically assigns node operators to suitable jobs based on their reputation scores and the creators’ specifications. Node operators can then use OctaneRender to access, process and complete the job according to its specifications. Creators can access the rendering in real-time and have the ability to flag discrepancies. Once the job is done, the creator then verifies and accepts the job. This whole process is called Proof of Render.
Completion/Payment
RNDR tokens are the primary mode of payment in the network. These tokens are held in escrow during the rendering job and are released to node operators once a creator confirms that the job is satisfactory. Render Network charges a small percentage of the payment for facilitating the transaction and running the network, which can vary between 0.5-5% of the total RNDR paid for the job. Once the rendering job is complete, OctaneRender can be used to download or share their rendered assets.
Security
Render Network places a strong emphasis on security. After uploading the job onto the network, it is broken down into separate files that are end-to-end encrypted and hashed, ensuring the ability to trace it and detect any malicious activities/attempts. The network also uses watermarks to ensure asset safety. This means that when a client uploads a 3D-rendering task, the files are viewable in a watermarked form until the client confirms that the job has been completed and pays for it. Once the payment is made, the network uses smart contracts to release the unwatermarked assets to the client and tokens to the node operator who did the job.
Finally, it uses a reputation score as the main indicator of a node operator’s quality. It is calculated based on factors such as jobs completed, job quality, job duration, and customer satisfaction ratings. A higher reputation score indicates that a node operator has a proven track record of delivering high-quality work in a timely manner and is, therefore, more likely to be selected for future jobs. All these security features create a trustless environment for users.
RNDR Tokenomics
RNDR, the native utility token of the Render Network, was launched in a public token sale in October 2017 and a private token sale lasting from January 2018 to May 2018. In December 2021, the network raised $30m in strategic funding led by Multicoin Capital, with support from Alameda Research and the Solana Foundation, bringing Render's total funds raised to an impressive $50m.
RNDR has a max supply of 531 million, with 364 million currently circulating in the market. It is used to pay for rendering services on the network and to incentivise node operators to provide computational power and contribute to the rendering process, essentially making it the only means of exchange in the ecosystem.
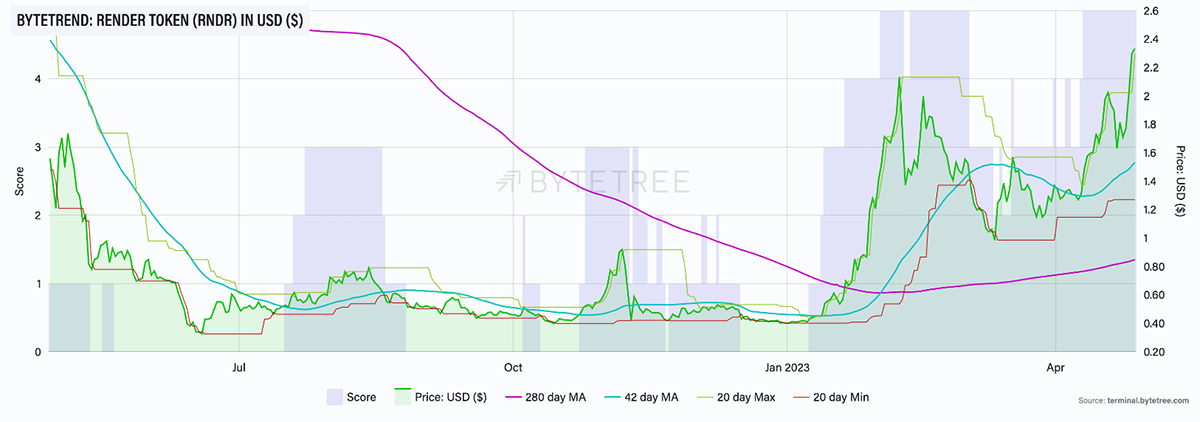
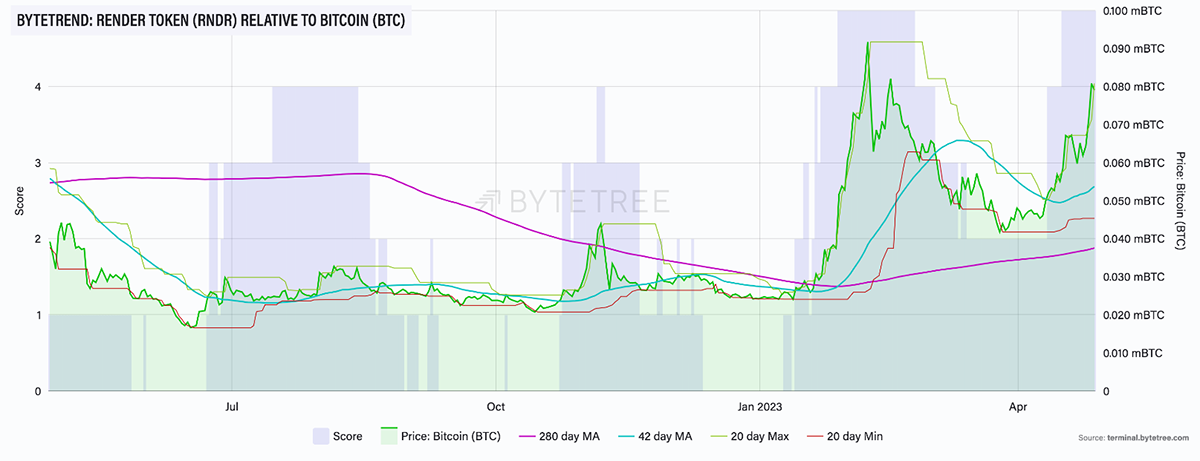
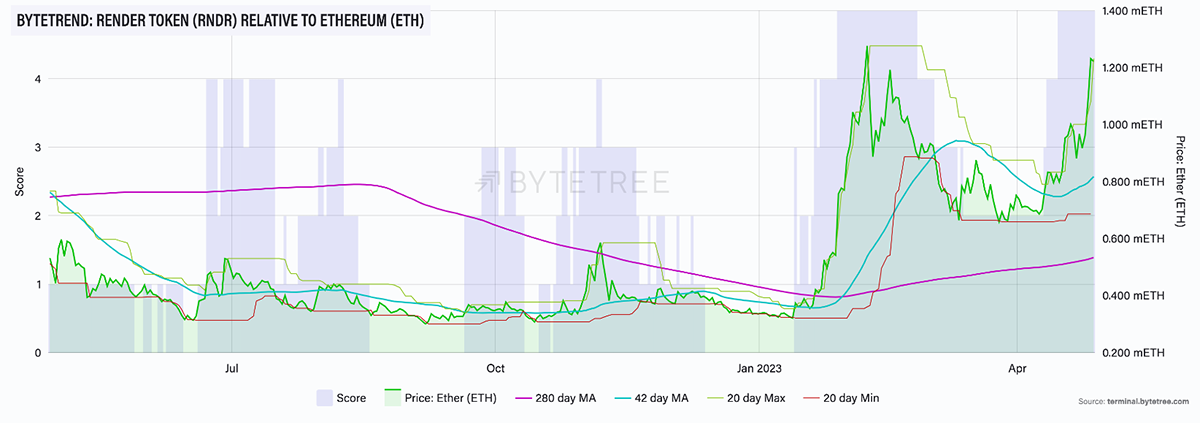
As illustrated in all the three charts above, RNDR is currently scoring a 5-star ByteTrend in USD, BTC and ETH, showcasing a strong bullish trend against the three major assets.
Competition
The Render Network faces a significant challenge from the competition. Several sizable and mid-sized companies offer centralised GPU cloud rendering services, such as Google Cloud, Azure, IBM Cloud, IRender, and Render Pool. Additionally, crypto-native projects such as SONM also provide decentralised cloud rendering solutions with competitive pricing and strong security.
Despite the strong competition, the Render Network aims to differentiate itself from centralised companies by providing a decentralised cloud rendering solution that offers greater security and more efficient resource allocation through its unique MTP protocol. The use of blockchain technology and smart contracts also ensures transparency and trust in the rendering process, which is lacking in centralised rendering services. Additionally, the Render Network's community-driven approach allows creators and node operators to have a say in the network's governance and direction, which fosters a sense of ownership and loyalty. Through these unique features, the Render Network hopes to stand out and add real value to the cloud rendering market.
Future
In December 2022, Render Network integrated the latest version of OctaneRender, Octane 2022. This integration allows the network to support all production workflows of OctaneRender, making it compatible with all versions of the software. The prior Octane version introduced several improvements, including sampling APIs, optimised scene graph traversal, and increased GPU memory management efficiency. With Octane 2022, Render Network can now improve the speed, performance, and accuracy of the render engine by introducing advanced features such as the Deep Learning Denoiser, which uses complex algorithms to reduce noise in rendered images, improved instancing performance, and a new material library. In 2023, Octane 2022 is expected to serve as the foundation for future developments in the Render Network.
The Render Network is currently exploring LightField Rendering as part of its efforts to expand its intensive rendering services. LightField rendering is a sophisticated computer graphics technique that creates 3D representations of real-world scenes by combining multiple views of a scene from different angles. These types of rendering jobs require more processing power and are more complex than other rendering jobs but have the potential to generate 10 to 100 times more demand for rendering services per job. Innovative upgrades like these present a significant opportunity for the Render Network to expand its customer base in the future.
Conclusion
Render is the leading decentralised, blockchain-powered GPU-rendering service provider in the industry. Its innovative approach enables node operators to monetise their idle GPU-computing capacity, resulting in efficient and widespread GPU usage. This cost-effective, secure, and trustless rendering service benefits creators tremendously. However, competing with traditional players is no easy feat for Render, especially with the emergence of decentralised rendering providers that pose a significant threat to its market position. Since the RNDR token is the backbone of the network, its success ultimately depends on the platform’s usage.

Comments ()